How To Change Image Size Relative To Its Original Size
If your epitome doesn't fit the layout, you tin can resize information technology in the HTML. One of the simplest ways to resize an image in the HTML is using the height and width attributes on the img tag. These values specify the acme and width of the image element. The values are prepare in px i.due east. CSS pixels.
For example, the original image is 640×960.
https://ik.imagekit.io/ikmedia/women-dress-ii.jpg 
We tin can render information technology with a height of 500 pixels and a width of 400 pixels
<img src="https://ik.imagekit.io/ikmedia/women-dress-ii.jpg" width="400" summit="500" /> 
If the image element's required height and width don't lucifer the image's actual dimensions, so the browser downscales (or upscale) the image. The exact algorithm used by the browser for scaling can vary and depends on the underlying hardware and Os.
There are a couple of downsides of client-side image resizing, mainly poor epitome quality and slower image rendering. To overcome this, you should serve already resized images from the server. You can use Thumbor or a gratis image CDN like ImageKit.io to resize images dynamically using URL parameters.
Resizing an epitome in CSS
You can besides specify the height and width in CSS.
img { width: 400px, acme: 300px } Preserving the aspect ratio while resizing images
When yous specify both acme and width, the image might lose its aspect ratio. Y'all can preserve the attribute ratio by specifying merely width and setting meridian to auto using CSS property.
img { width: 400px, pinnacle: machine } This will render a 400px broad epitome. The height is adapted accordingly to preserve the attribute ratio of the original image. You tin can as well specify the elevation aspect and set width as auto, but most layouts are more often than not width constrained and not peak.
Responsive image which adjusts based on available width
You lot tin specify the width in percentage instead of an absolute number to make it responsive. By setting width to 100%, the image volition scale up if required to match the parent element'south width. It might result in a blurred image every bit the prototype can be scaled up to exist larger than its original size.
img { width: 100%; height: auto; } Alternatively, you can utilize the max-width property. By setting
max-width:100%; the epitome will calibration down if information technology has to, but never scale up to exist larger than its original size.
img { max-width: 100%; height: automobile; } How to resize & crop paradigm to fit an element area?
So far, we have discussed how to resize an prototype by specifying acme or width or both of them.
When y'all specify both pinnacle and width, the paradigm is forced to fit the requested dimension. It could change the original aspect ratio. At times, you want to preserve the aspect ratio while the paradigm covers the whole area even if some part of the image is cropped. To reach this, you can use:
- Background image
-
object-fitcss holding
Resizing background image
background-paradigm is a very powerful CSS property that allows you to insert images on elements other than img. You can control the resizing and cropping of the image using the post-obit CSS attributes-
-
background-size- Size of the image -
background-position- Starting position of a background prototype
groundwork-size
By default, the background epitome is rendered at its original full size. You can override this by setting the height and width using the background-size CSS property. Y'all tin can scale the image upward or downward as you lot wish.
<fashion> .background { background-image: url("/epitome.jpg"); background-size: 150px; width: 300px; height: 300px; border: solid 2px crimson; } </style> <div course="background"> </div> Possible values of groundwork-size:
-
auto- Renders the image at full size -
length- Sets the width and superlative of the background paradigm. The first value sets the width, and the second value sets the peak. If just one value is given, the second is set toauto. For example,100px 100pxor50px. -
percentage- Sets the width and height of the background prototype in per centum of the parent element. The first value sets the width, and the 2d value sets the height. If only one value is given, the 2nd is set toauto. For example,100% 100%or50%.
It also has ii special values comprise and cover:
background-size:contains
contains - It preserves the original aspect ratio of the image, but the epitome is resized and so that it is fully visible. The longest of either the height or width will fit in the given dimensions, regardless of the size of the containing box.
<way> .background { groundwork-paradigm: url("/image.jpg"); groundwork-size: contains; width: 300px; height: 300px; border: solid 2px blood-red; } </style> <div grade="background"> </div> background-size:encompass
cover - It preserves the original aspect ratio but resizes the image to encompass the entire container, fifty-fifty if it has to upscale the prototype or crop it.
<fashion> .background { background-image: url("/epitome.jpg"); background-size: encompass; width: 300px; top: 300px; edge: solid 2px red; } </style> <div form="background"> </div> object-fit CSS belongings
Y'all can employ the object-fit CSS property on the img chemical element to specify how the epitome should be resized & cropped to fit the container. Before this CSS holding was introduced, nosotros had to resort to using a background image.
Forth with inherit, initial, and unset, there are 5 more possible values for object-fit:
-
incorporate: It preserves the original aspect ratio of the image, but the prototype is resized and then that it is fully visible. The longest of either the tiptop or width will fit in the given dimensions, regardless of the size of the containing box. -
cover: Information technology preserves the original aspect ratio but resizes the image to cover the entire container, even if it has to upscale the image or ingather it. -
fill: This is the default value. The image volition fill its given expanse, even if it means losing its aspect ratio. -
none: The image is non resized at all, and the original image size fills the given surface area. -
scale-down: The smaller of either incorporate or none .
You can employ object-position to control the starting position of the paradigm in example a cropped part of the paradigm is beingness rendered.
Permit's sympathise these with examples.
The following prototype's original width is 1280px and height is 854px. Here information technology is stretching to maximum bachelor width using max-width: 100%.
<img src="https://ik.imagekit.io/ikmedia/backlit.jpg" style="max-width: 100%;" /> 
object-fit:contains
<img src="https://ik.imagekit.io/ikmedia/backlit.jpg" style="object-fit:contain; width:200px; superlative:300px; border: solid 1px #CCC"/> The original aspect ratio of the image is aforementioned, but the epitome is resized so that it is fully visible. We take added 1px border around the paradigm to showcase this.

object-fit:cover
<img src="https://ik.imagekit.io/ikmedia/backlit.jpg" style="object-fit:cover; width:200px; height:300px; border: solid 1px #CCC"/> The original aspect ratio is preserved simply to embrace the whole area image is clipped from the left and right side.

object-fit:fill
<img src="https://ik.imagekit.io/ikmedia/backlit.jpg" style="object-fit:make full; width:200px; peak:300px; border: solid 1px #CCC"/> Image is forced to fit into a 200px broad container with height 300px, the original aspect ratio is non preserved.

object-fit:none
<img src="https://ik.imagekit.io/ikmedia/backlit.jpg" fashion="object-fit:none; width:200px; superlative:300px; border: solid 1px #CCC"/> 
object-fit:calibration-down
<img src="https://ik.imagekit.io/ikmedia/backlit.jpg" manner="object-fit:scale-downwards; width:200px; peak:300px; edge: solid 1px #CCC"/> 
object-fit:encompass and object-position:right
<img src="https://ik.imagekit.io/ikmedia/backlit.jpg" style="object-fit:encompass; object-position: right; width:200px; height:300px; border: solid 1px #CCC"/> 
Downsides of customer-side paradigm resizing
There are certain downsides of client-side resizing that yous should proceed in mind.
i. Dull image rendering
Since the full-sized image is loaded anyhow before resizing happens in the browser, it takes more than time to finish downloading and finally rendering. This means that if yous take a large, 1.5 megabyte, 1024×682 photograph that you are displaying at 400px in width, the whole ane.v-megabyte image is downloaded past the visitor before the browser resizes it downwards to 400px.
Yous can see this download time on the network panel, as shown in the screenshot below.
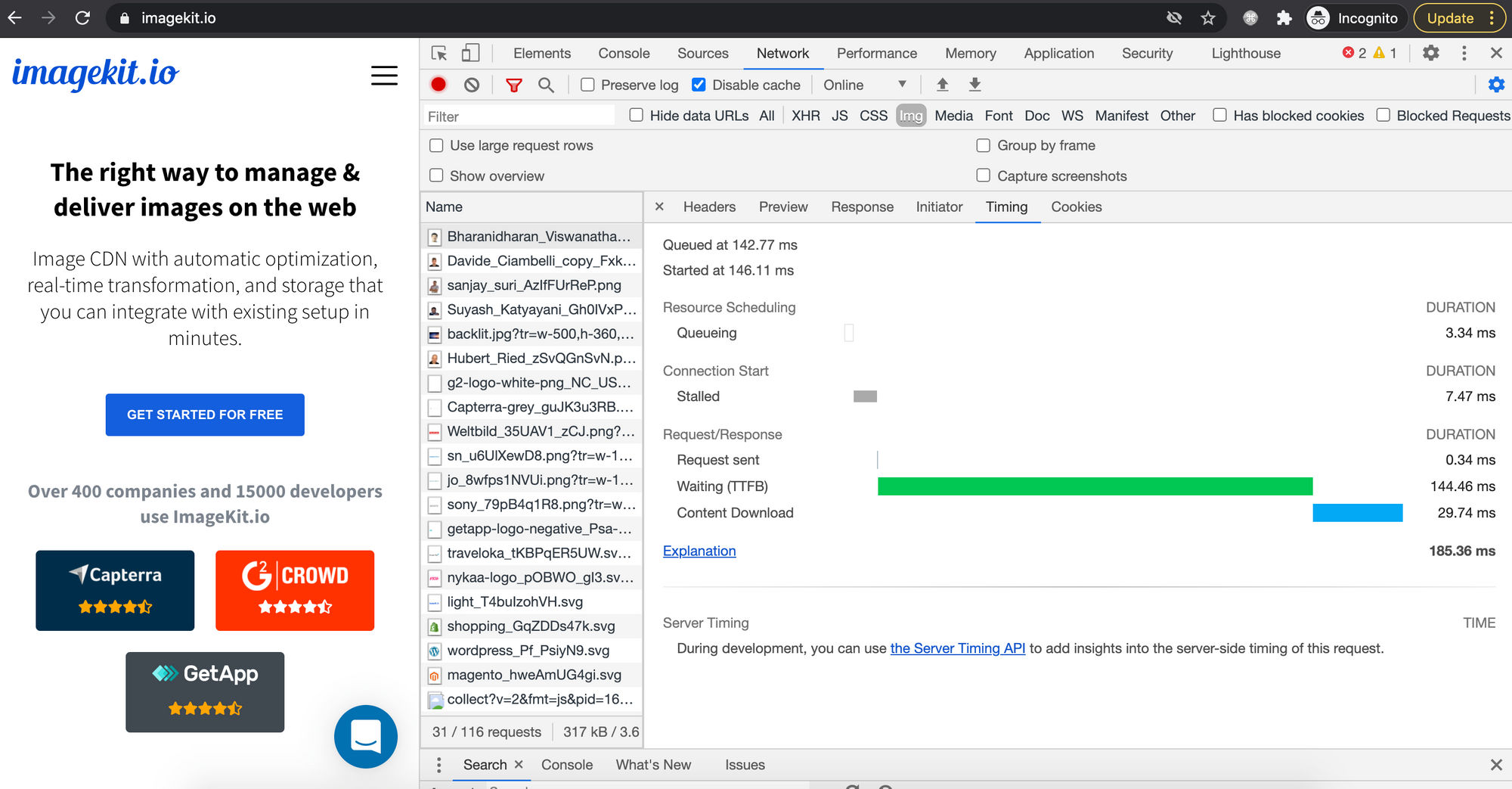
On the other hand, if you resize the image on the server using some program or an image CDN, then the browser doesn't have to load a large corporeality of data and waste material time decoding & rendering it.
With ImageKit.io, yous can easily resize an image using URL parameters. For instance -
Original paradigm
https://ik.imagekit.io/ikmedia/women-dress-2.jpg
400px broad prototype with aspect ratio preserved
https://ik.imagekit.io/ikmedia/women-clothes-2.jpg?tr=westward-400
2. Poor image quality
The exact scaling algorithm used by the browser can vary, and its performance depends upon underlying hardware and Os. When a relatively bigger epitome is resized to fit a smaller container, the terminal image could exist noticeably blurry.
There is a tradeoff between speed and quality. The final pick depends upon the browser. Firefox 3.0 and after versions use a bilinear resampling algorithm, which is tuned for high quality rather than speed. Merely this could vary.
You can use the image-rendering CSS property, which defines how the browser should render an image if information technology is scaled upwardly or down from its original dimensions.
/* Keyword values */ image-rendering: car; prototype-rendering: crisp-edges; prototype-rendering: pixelated; /* Global values */ image-rendering: inherit; image-rendering: initial; image-rendering: unset; three. Bandwidth wastage
Since the total-sized epitome is being loaded anyway, information technology results in wastage of bandwidth, which could take been saved. Data transfer is non inexpensive. In addition to increasing your bandwidth bills, information technology too costs your users real money.
If you are using an prototype CDN, you tin further reduce your bandwidth consumption by serving images in next-gen formats e.g. WebP or AVIF.
The user friendly dashboard will as well show you how much bandwidth you have saved so far

iv. Increased retention and processing requirements on client devices
Resizing large images to fit a smaller container is expensive and can be painful on low-end devices where both retentivity and processing power is limited. This slows down the whole spider web page and degrades the user experience.
Summary
When implementing web pages, images need to fit the layout perfectly. Here is what y'all need to think to exist able to implement responsive designs:
- Avoid customer-side (browser) resizing at all if you lot can. This means serve correctly sized images from the server. It results in less bandwidth usage, faster image loading, and higher image quality. At that place are many open-source image processing libraries if yous want to implement it yourself. Or meliorate, you can use a complimentary epitome CDN which volition provide all these features and much more with a few lines of code.
- Never upscale a raster epitome i.e. JPEG, PNG, WebP, or AVIF images, should never be upscaled as information technology volition result in a blurred output.
- You should apply the SVG format for icons and graphics if required in multiple dimensions in the pattern.
- While resizing, if y'all want to preserve the attribute ratio of original images - Only specify 1 of
widthandheightand set the other toauto. - If you want the image to fit the entire container while preserving the attribute ratio, even if some role is cropped or the image is upscaled - Utilise the
object-fitCSS property or set a background image using thebackground-epitomeCSS property. - Control the starting position of the image using
object-positionwhile usingobject-fit. In background images, usebackground-position.
Source: https://imagekit.io/blog/how-to-resize-image-in-html/
Posted by: laforestoulds1946.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Change Image Size Relative To Its Original Size"
Post a Comment